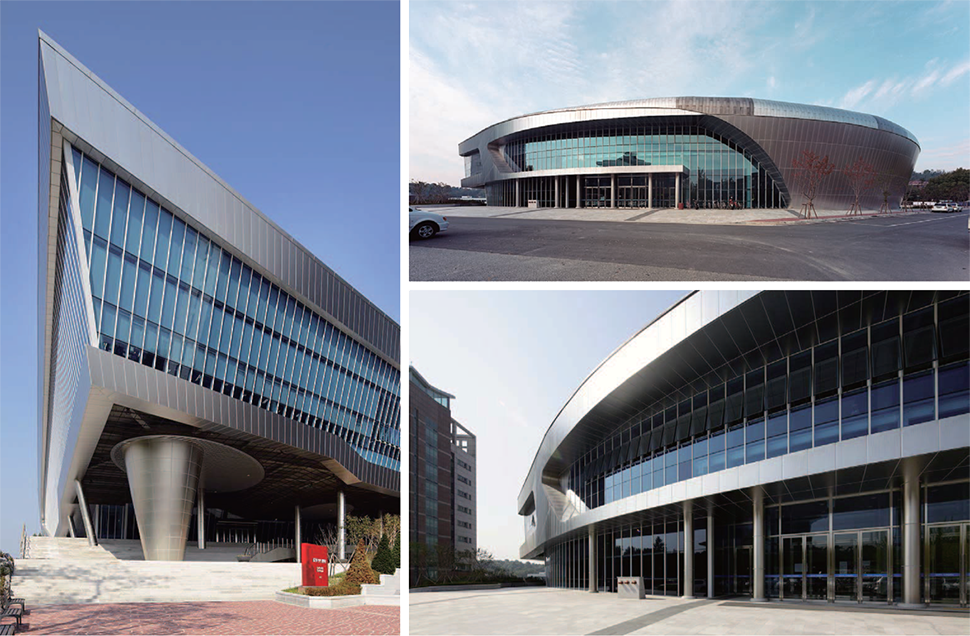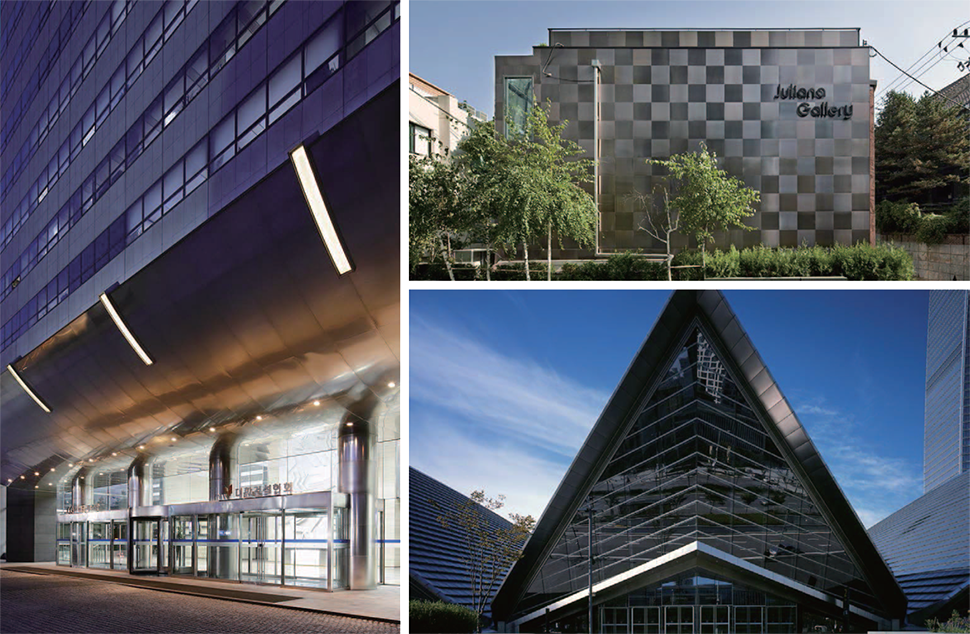
Titanium color coil is manufactured using the physical deposition method where a chunk of titanium is placed into high vacuum to produce coating. This cutting-edge functional product is playing an important role in many areas including automotive, electrical and electronic industries.
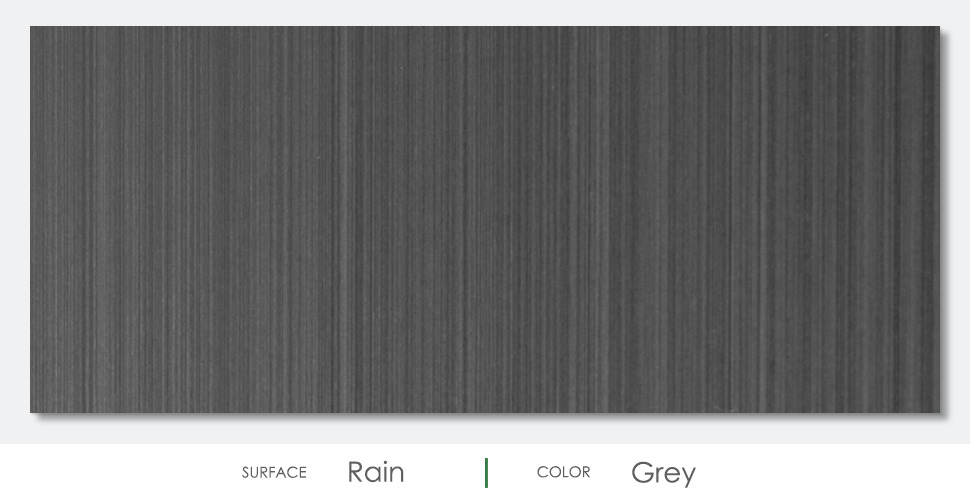
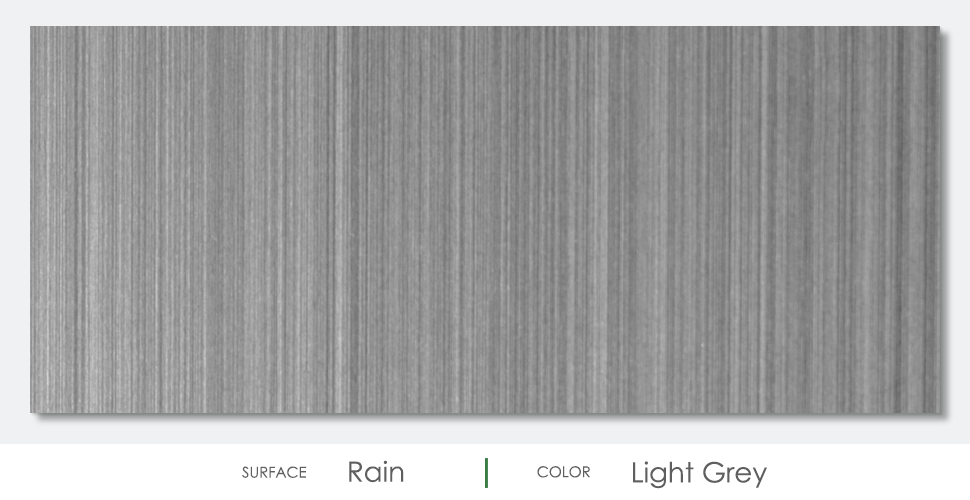











Color









Surface Finish


Product Specifications
| Steel Grade | 201, 202, 304, 316, 316L | |
|---|---|---|
| Surface material | No.4 | Hard Bead Blast |
| Thickness of surface material | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Width / Length | From 600 to 1000/2400 | |
| Thickness of Steel back material | STS (Steel Grade 400) - 0.6 / 0.8 / 1.0 / 1.2 / 1.5 EGI, ZAM (0.6 / 0.8 / 1.0 / 1.2 / 1.6) |
|
Various, uniform colors available. Economical mass production.
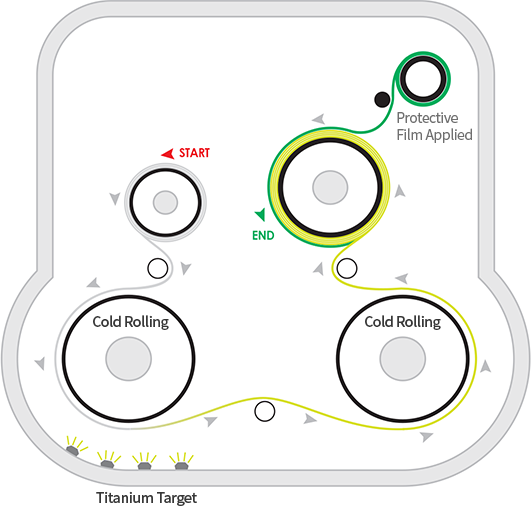
What is Titanium Color Coating?


This coating technique uses the physical deposition method, where titanium alkoxide (lump of titanium) is placed in high vacuum. Then + voltage is applied to titanium and - voltage is applied to the product that needs to be coated. This generates titanium particles that, in high vacuum, adhere to the product under - voltage forming its coating.
Metal is evaporated in the vacuum using different sources of energy like an arc, heat, electronic load, then activated using plasma or ion beam to form the required surface. There are several methods that are used to evaporate metal and increase its reactivity during the coating process. For heavy and large parts like tools or molds, plasma cleaning and ion bombardment are required to increase the adherence.
How effective the cleaning and coating process is affects the performance and longevity of the molds and tools being manufactured. The recent development of the PVD technology resulted in a new process technology allowing for a significant progress to be made. And this cutting-edge functional surface treatment method has greatly benefited several areas including the automotive, electrical and electronic industries.
Characteristics of titanium color coating
The hardness of the thin film of this product measured with the Micro Vickers tester is at least 10 times higher than that of stainless steel.
As a result of performing the peel test by scratching the product with a knife at an interval of 2 mm and putting cellophane tape on the surface, no film peeling was observed.
As a result of visual assessment by observation after a 1-kg steel ball dropped on the product from the height of 50 cm by using the DuPont impact tester, there was no damage or discoloration.
| Hardness(HV) | |
|---|---|
| Ion Plating | 2250 |
| Stainless(304) | 150~170 |
As a result of applying a load of 500g on an eraser by using a SUGA rotational abrasion tester on the surface with thickness of 0.5 micron for ion plating and wearing it down for 200 repetitive cycles, the color reaction of chemical compounds were exposed but ion-plated films were not peeled off.
As a result of visually observing the change in the color of the ion-plated material after being left for 500 hours at the temperature of 50°C and the humidity of 98%, no problem was found.
Below is the load at the moment that scratches start to appear from ion plating scratched at the speed of 150 mm/min by using the Clemens type scratch hardness tester. Ion plating has by 3 times higher scratch hardness than chemical plating.
| Scratch Hardness | |
|---|---|
| Ion Plating | 15.7N |
| Chemical Plating | 4.9N |
Artificial sweat liquid similar to human sweat (PH 4.5. JIS LO848) is prepared. Ion-plated frame is then submerged in at a room temperature for 8 hours. Afterwards, it‘s removed and left to dry in room temperature for 16 hours. The table shows the results obtained when this sequence is repeated 7 times. No corrosion of ion plating from artificial sweat occurred on the metal plate.
| Artificial sweat resistance | Evaluation | |
|---|---|---|
| Ion Plating | Gold | No abnormalities |
| Brass | No clear | Partial pitting corrosion confirmed |
| No clear | Corrosion in several parts confirmed | |
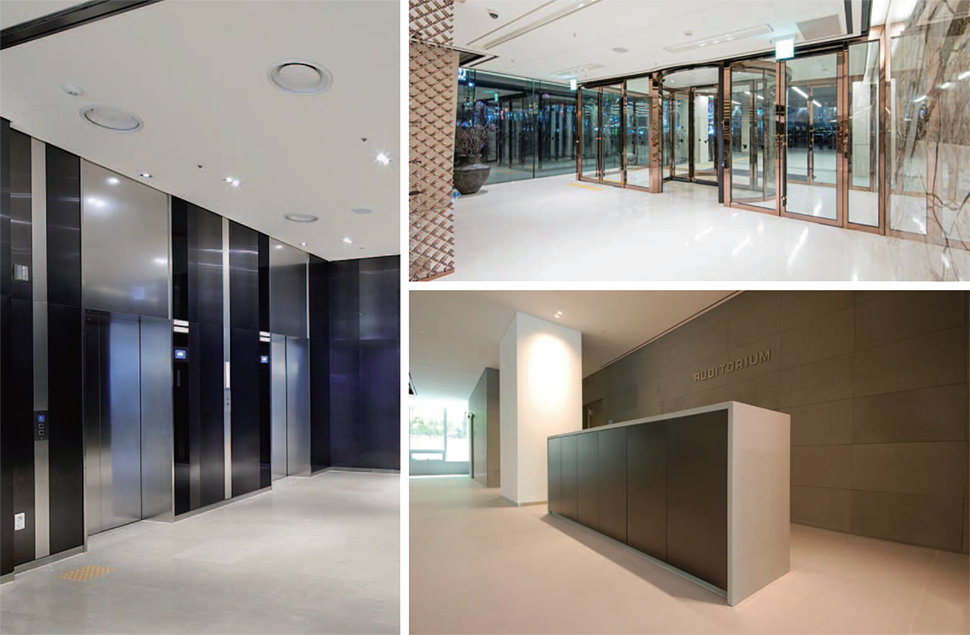
Interior material
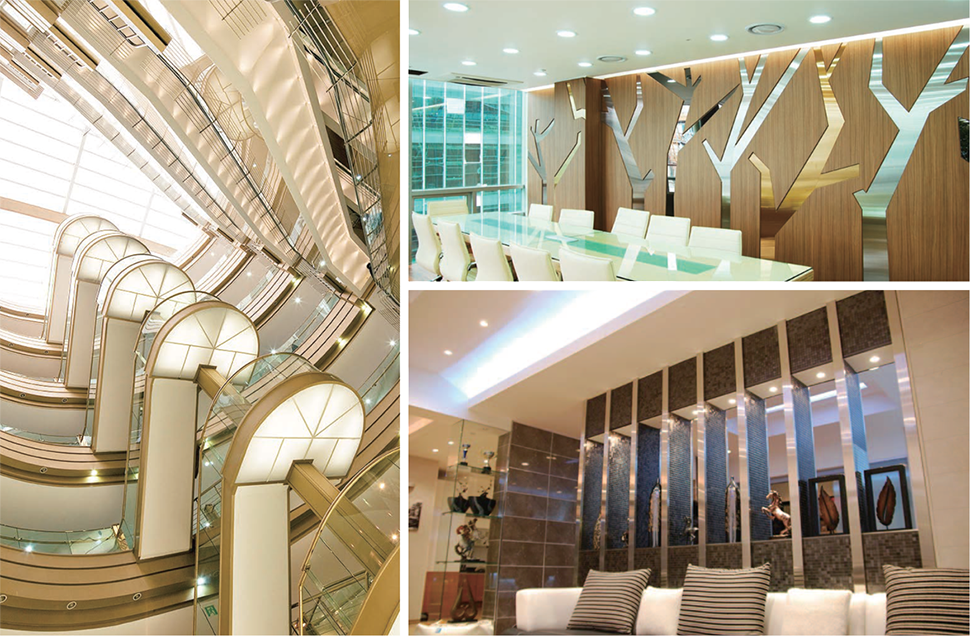


Exterior material

